Everybody needs to eat, so demand for food — especially good food — will never go away. This helps explain why the food industrycontinue ...
You should consider creating a niche for yourself by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry.
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on May 4, 2021

Investment range
$12,550 - $22,100
Revenue potential
$100,000 - $312,000 p.a.
Time to build
1 - 3 months
Profit potential
$36,000 - $47,000 p.a.
Industry trend
Growing
Commitment
Full-time
Here are the most essential aspects to consider when starting your meal prep business:
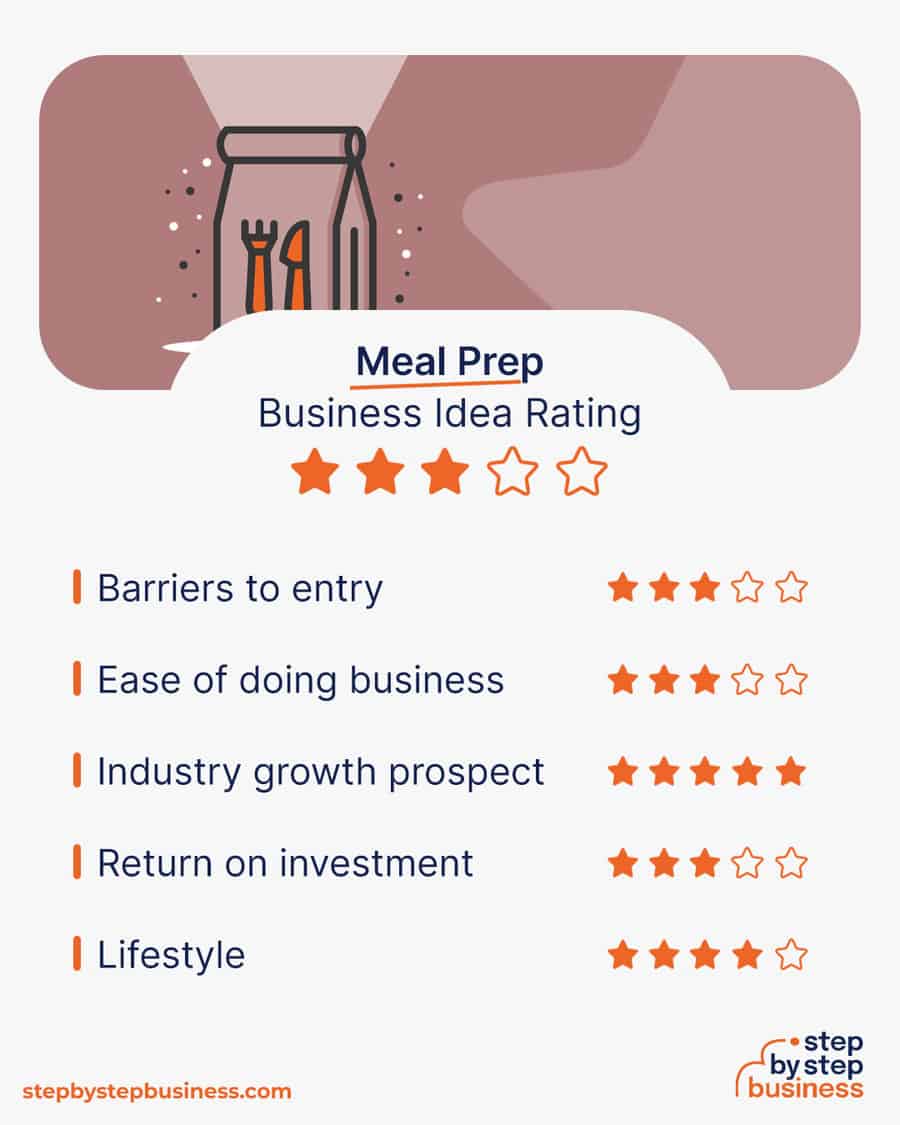
It makes perfect sense to know what you’re getting into before you take the plunge. Without an in-depth understanding of the industry, you can never be sure if your idea will be profitable and sustainable.
Understand the pros and cons of starting a meal delivery service to make sure the idea is worth your time and money.
Several factors are driving sharp growth in pre-made meal deliveries, including increased preference among millennials for homemade meals and greater familiarity with delivery and mobile apps among younger generations. In addition, it’s one of the few industries that was boosted by the pandemic, as nearly all restaurants were shut down, forcing people to eat at home with much greater frequency. Finally, people are more health-conscious today than ever before, and meal kit delivery caters to these consumers.


These are the latest trends in the industry:
Some of the challenges faced by meal prep operators are:
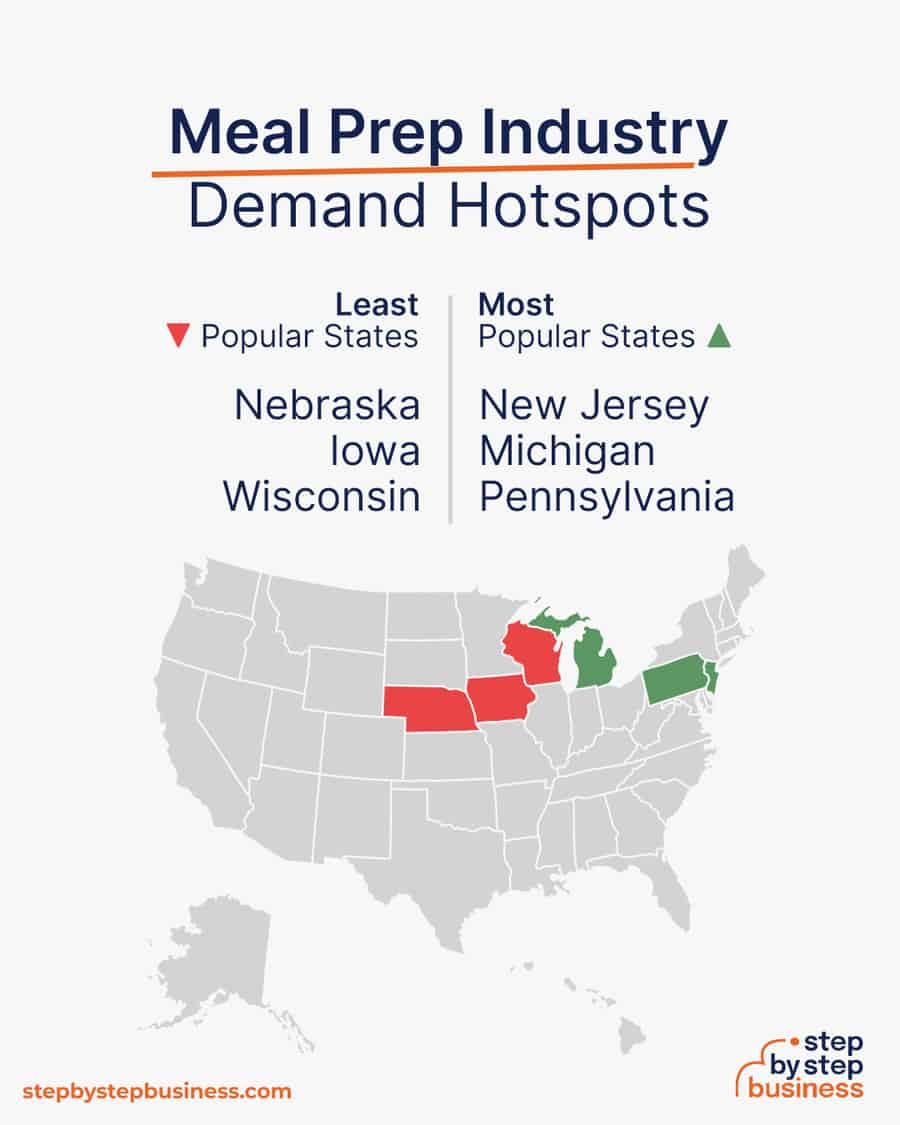

The most important role in a meal prep business is the chef.
Starting a home-based meal prep business can cost as little as $1,000, though it’s probably best to start your business in a commercial setting. For this, you’ll need to spend at least $8,000, and potentially as much as $30,000, to get your business off the ground.
A typical meal delivery startup will incur these costs:
| Start-up Costs | Ballpark Range | Average |
|---|---|---|
| Setting up a business name and corporation | $150 - $200 | 175 |
| Business licenses and permits | $100 - $300 | 200 |
| Business cards and brochures | $200 - $300 | 250 |
| Kitchen equipment | $5,000 - $8,000 | $6,500 |
| Initial supplies | $3,000 - $5,000 | $4,000 |
| Package design | $2,000 - $3,000 | $2,500 |
| Insurance | $100 - $300 | 200 |
| Rent | $1,000 - $2,000 | $1,500 |
| Website setup | $1,000 - $3,000 | 2000 |
| Total | $12,550 - $22,100 | $17,325 |
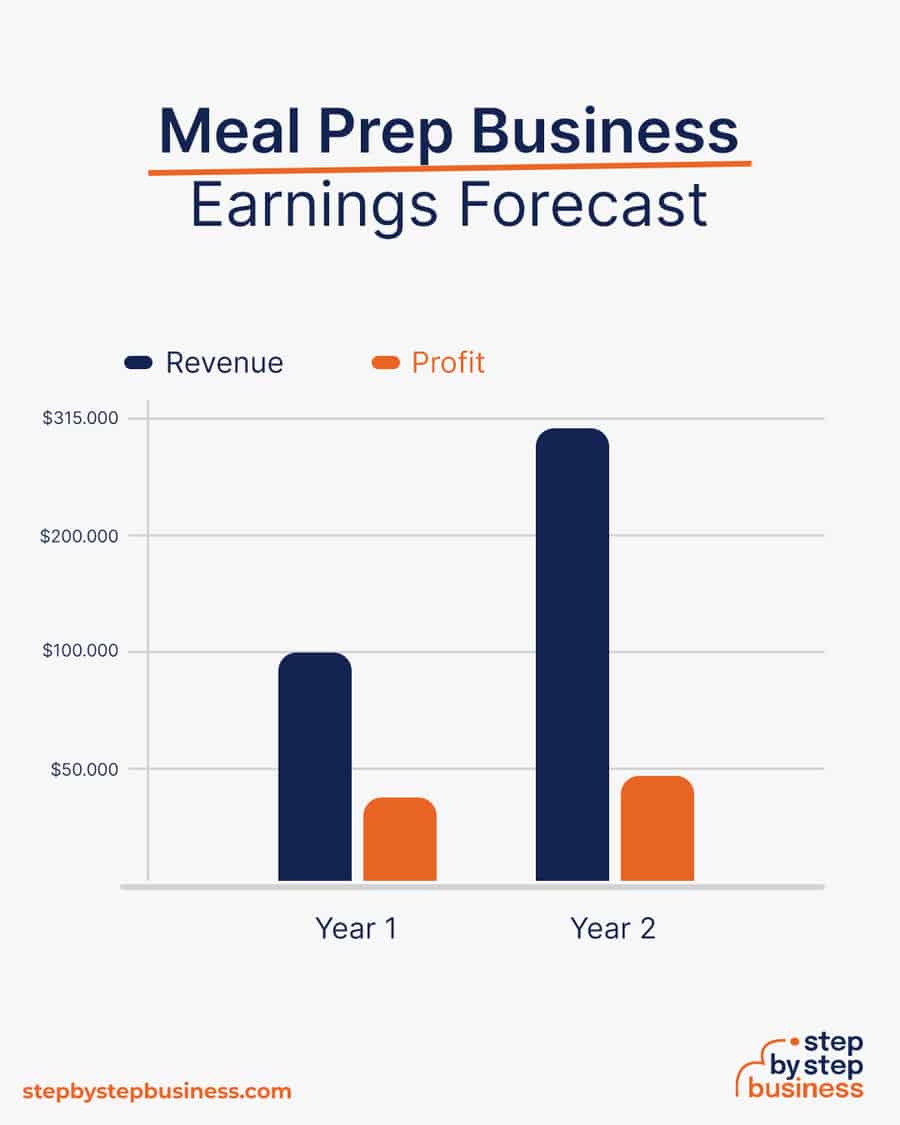
The average profit margin for a food delivery business is 15-35%.
In your first year or two, you could have 20 clients who order two meals a day at $10 each for five days a week, bringing in more than $100,000 in annual revenue. This would mean $36,000 in profit, assuming that 35% margin. As your brand gains recognition, sales could climb to 100 meals a day and your operating hours are extended to six days a week. At this stage, you’d have to hire additional staff and move to a bigger commercial space, reducing your profit margin to around 15%. With annual revenue of $312,000, you’d make a tidy profit of $47,000.
Like any business, there are challenges you’re likely to encounter when trying to venture into the meal prep business. These include:
With the basics out of the way, it’s time to drill down on meal prep delivery business specifics.
Market research will give you the upper hand, even if you’re already positive that you have a perfect product or service. Conducting market research is important, because it can help you understand your customers better, who your competitors are, and your business landscape.
Meal delivery is a highly competitive industry, so you’ll want to do a competitive analysis to determine your competition’s strengths and weaknesses. Your direct competitors will be restaurants and food outlets that offer meal delivery services to their customers, as well as other meal prep businesses in the area.
Examine their prices, their product offerings, their delivery timelines and subscription models, to get an idea of what’s out there.
Some viable meal preparation business models you can evaluate include on-demand delivery, goal-oriented meal delivery, and pre-cooked storable meal delivery.
Under the on-demand delivery model, customers order food on an on-demand basis. The goal-oriented delivery model focuses on customers with dietary restrictions or healthier lifestyle goals through weekly or monthly delivery subscriptions. It involves prepping meals using handpicked ingredients as per the customer’s needs.
The pre-cooked storable meal delivery model involves preparing pre-cooked and frozen meals such as burritos, pizzas, and other dishes.
You should consider creating a niche for yourself by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry.
This could jumpstart your word-of-mouth marketing within your niche market.
You’ll want to have different pricing tiers based on the number of meals ordered. Research what your competitors are charging to help you determine your pricing structure. The standard price for meals in this market is:
To break even, you should charge between $10 and $12 for a single serving. Still, you can sell at a higher price depending on your niche and ingredients.
Once you know your costs, you can use this Step By Step profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
The primary customers for a meal delivery business include students, busy professionals, young families, and remote workers. Depending on your business model, you may want to target consumers on special diets by focusing on meals with handpicked ingredients.
In the early stages, you may want to run your business from home to keep costs low. But as your business grows, you’ll likely need to hire workers for various roles and may need to rent out a production facility. You can find commercial space to rent in your area on sites such as Craigslist, Crexi, and Instant Offices.
When choosing a commercial space, you may want to follow these rules of thumb:
Ideally, you want a spot that allows you to deliver meals on time to as many customers as possible and maintain a high quality of meals on arrival.
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
Discover over 220 unique meal prep business name ideas here. If you want your business name to include specific keywords, you can also use our meal prep business name generator. Just type in a few keywords and hit “generate” and you’ll have dozens of suggestions at your fingertips.
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool below. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead with domain registration and social media account creation. Your business name is one of the key differentiators that set your business apart. Once you pick your company name, and start with the branding, it is hard to change the business name. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider your choice before you start a business entity.
Here are the key components of a business plan:
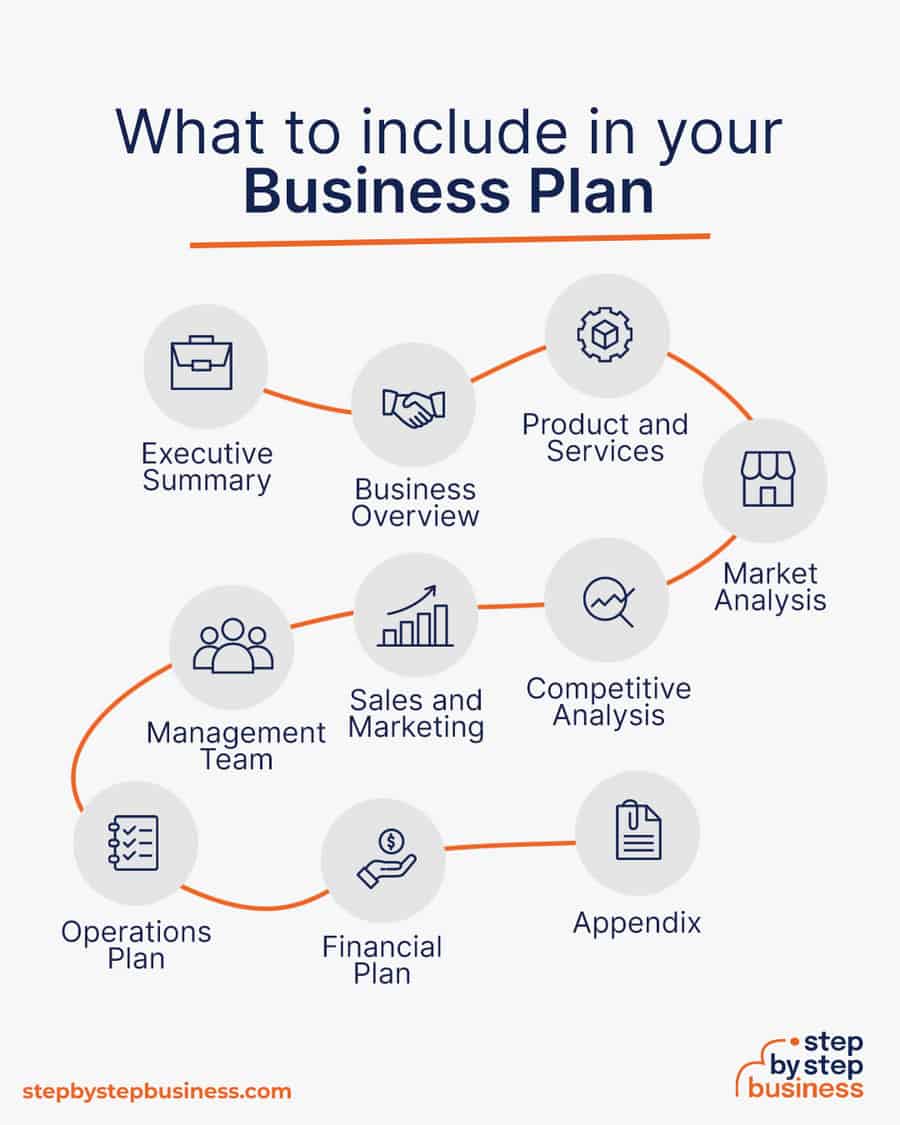
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you are planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to meal preparation.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your meal business will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
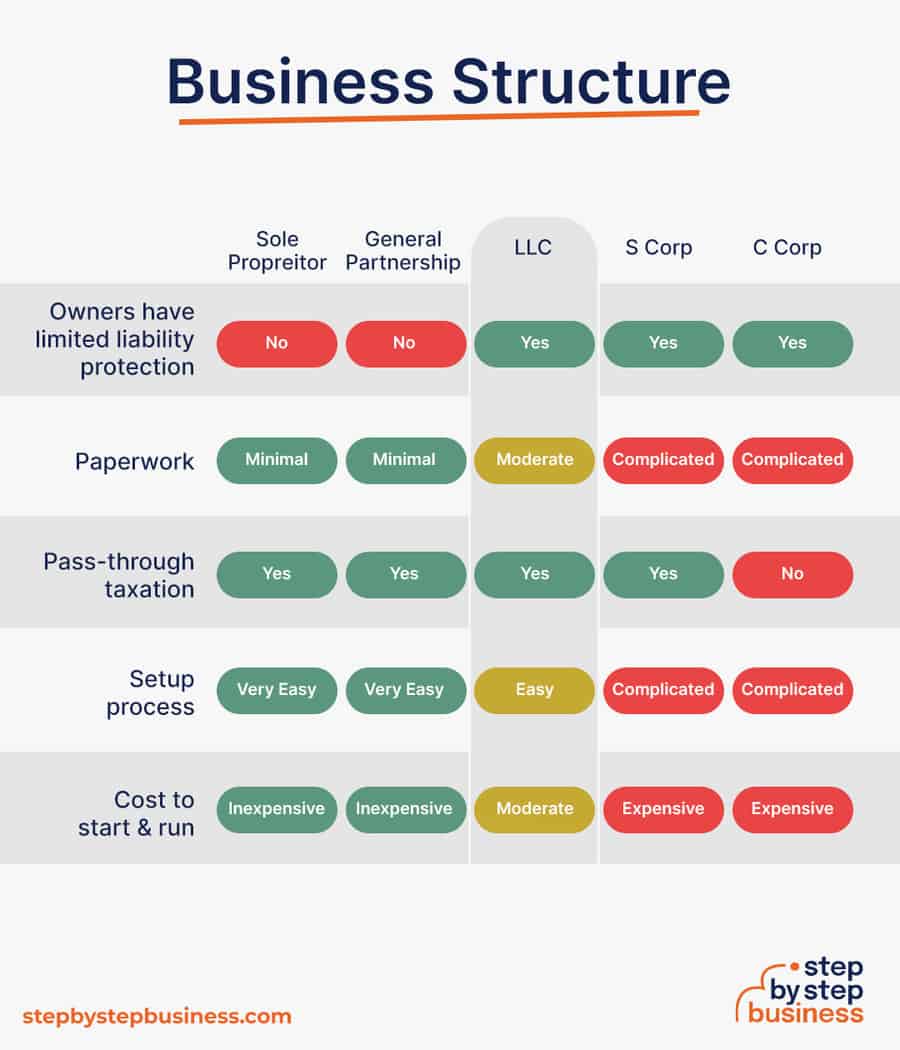
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization, and answer any questions you might have.
Choose Your State
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number, or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship, you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist, and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you are completing them correctly.
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
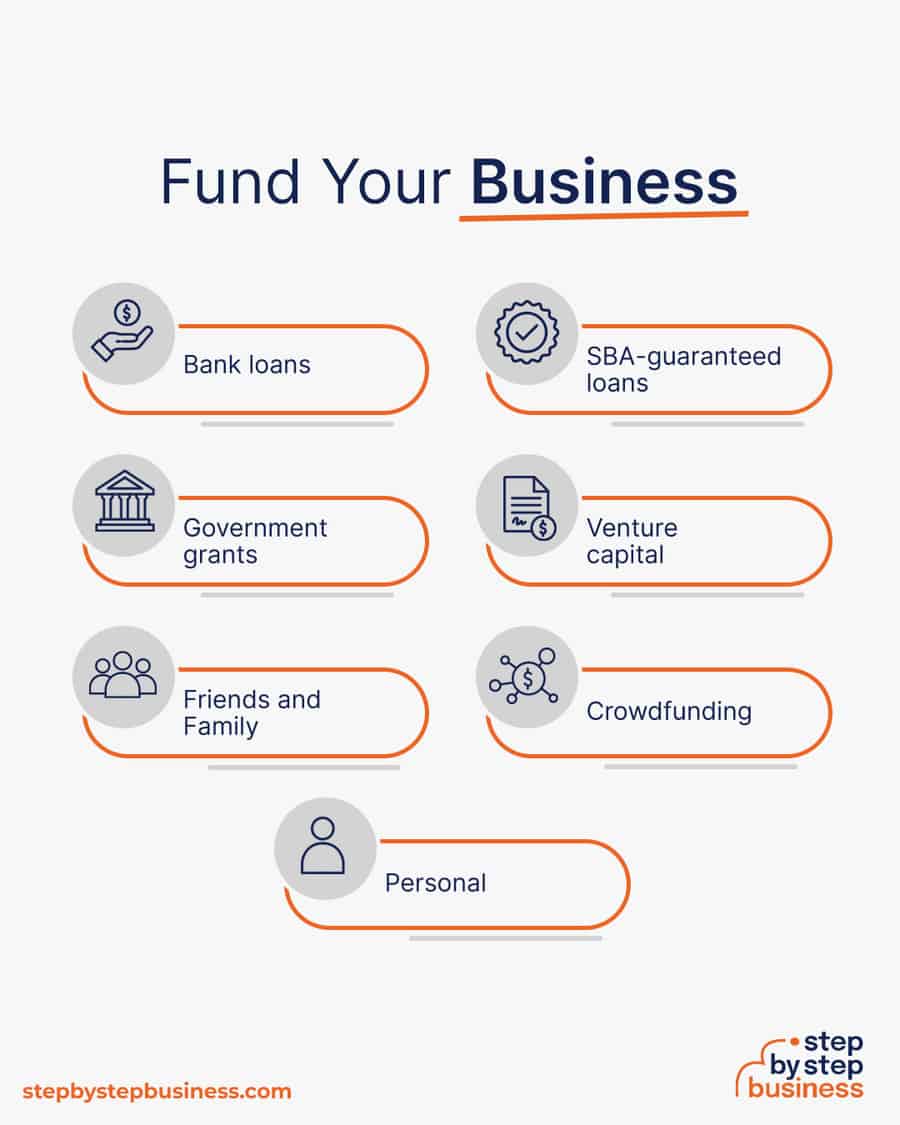
Bank and SBA loans are probably the best options, other than friends and family, for funding a meal preparation business. You might also try crowdfunding if you have an innovative concept.
Starting a meal prep business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package. They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Before you start making money you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account.
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your meal prep business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
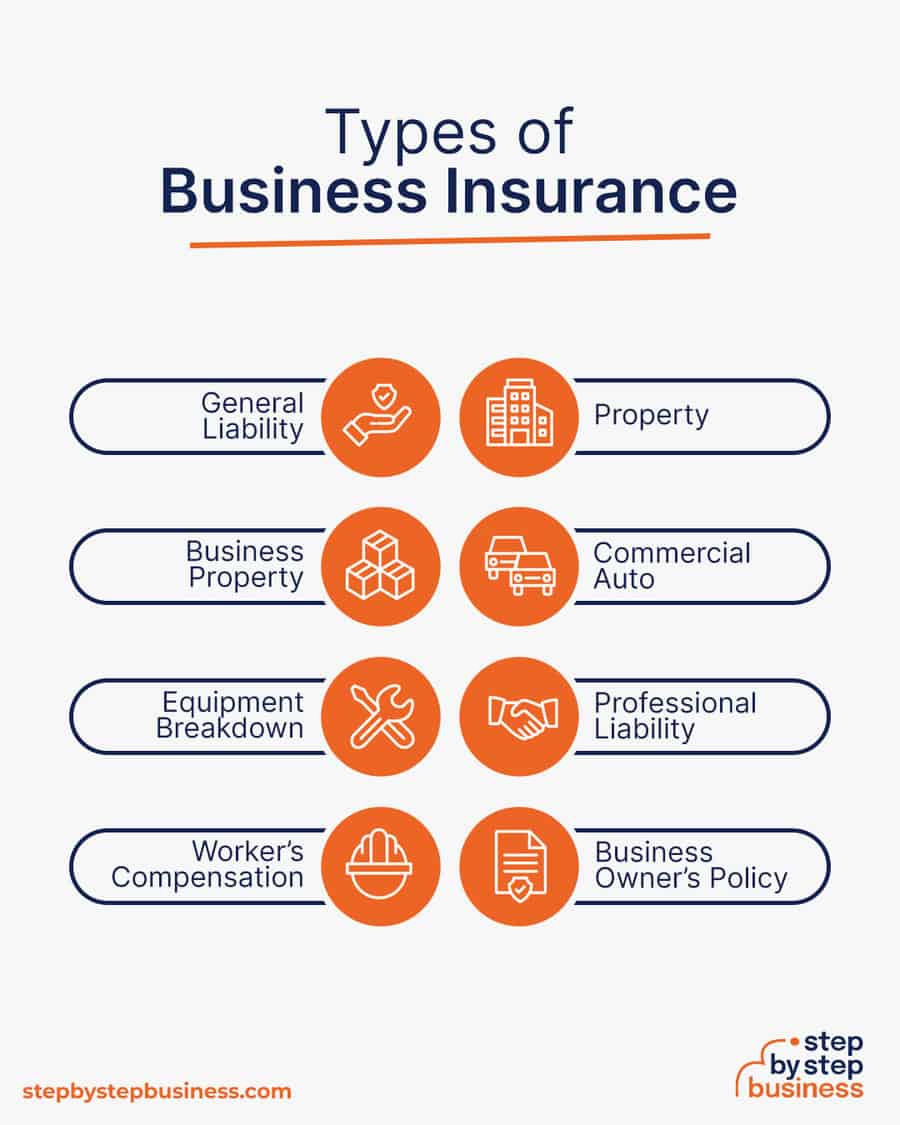
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use industry-specific software, such as Sprwt, KitchenFuel, and NutriBot to build your menu, manage your customers’ orders, and plan your logistics, among other things.
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism.
You can create your own website using services like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace. This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
They are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization (SEO) practices. These are steps that help pages rank higher in the results of top search engines like Google.
Starting a meal prep business can be a rewarding venture, and adopting effective marketing strategies is key to its success. Here are some proven and effective marketing strategies tailored for your meal prep business:

Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that set it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your meal kits meet their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Some signature USPs for your meal prep business could be:
You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running a meal prep business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been working in meal preparation for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in meal kits. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership. Online businesses might also consider affiliate marketing as a way to build relationships with potential partners and boost business.
If you’re starting out small from home, you may not need any employees. But as your business grows, you will likely need workers to fill various roles. Potential positions for a meal prep business would include:
At some point, you may need to hire all of these positions or simply a few, depending on the size and needs of your business. You might also hire multiple workers for a single role or a single worker for multiple roles, again depending on need.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed, Glassdoor, or ZipRecruiter. Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Operating a meal cooking service is relatively simple. It involves checking the orders customers have made on your website or through calls, prepping ingredients, cooking the dishes, and finally delivering the meals. The industry has already experienced exponential growth over the past five years due to the rise of online meal delivery and changing consumer preferences. This is an industry that is just starting to take off.
You should now know what you need to do to start a meal prep business, and it’s time to go out and execute! But just to be safe, you may want to bookmark this guide and return when needed to be sure you stay on track for success.
Even though pricing may vary, you should charge between $10 and $12 per serving. Of course, you can charge more depending on the type of meal. For example, organic or premium ingredients can fetch higher prices because the ingredients are more expensive.
Yes. It is. The business can generate higher profit margins than restaurants. With a profit margin of 15 to 35 percent, you can make a profit of $1,800 to $4,200, selling just 1,000 meal kits per month.
To give a perspective of what’s possible in this industry, HelloFresh, one of the biggest meal delivery companies in the United States, generates $2 billion in revenue per year while Cameron’s Seafood grosses $20 million annually.
To get customers for meal prep, utilize targeted marketing, offer referral programs, collaborate with local wellness centers or gyms, and emphasize the convenience of your services.
Meal prep food typically lasts for 3-4 days when stored properly in the refrigerator. Ensure proper storage conditions and thorough reheating before consuming.
Best foods for meal prep include lean proteins like chicken or tofu, whole grains such as brown rice or quinoa, vegetables like broccoli or spinach, fruits like berries or apples, and healthy fats such as avocado or nuts.
Differentiate your meal prep business by offering a diverse menu variety, catering to different dietary preferences and restrictions, using high-quality ingredients, focusing on customization and personalization, providing exceptional customer service, and highlighting unique features such as themed meal plans or specialized menus for specific health goals.

Published on July 21, 2022
Everybody needs to eat, so demand for food — especially good food — will never go away. This helps explain why the food industrycontinue ...
Read Now

Published on June 30, 2022
People are always eating and drinking, so starting a food business is always a potentially wise career choice. But to succeed you’ll need astr ...
Read Now
Published on June 8, 2022
Food trucks have exploded in popularity in recent years and offer a unique, potentially lucrative alternative to brick-and-mortar restaurants. Foodt ...
Read Now
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
Comments